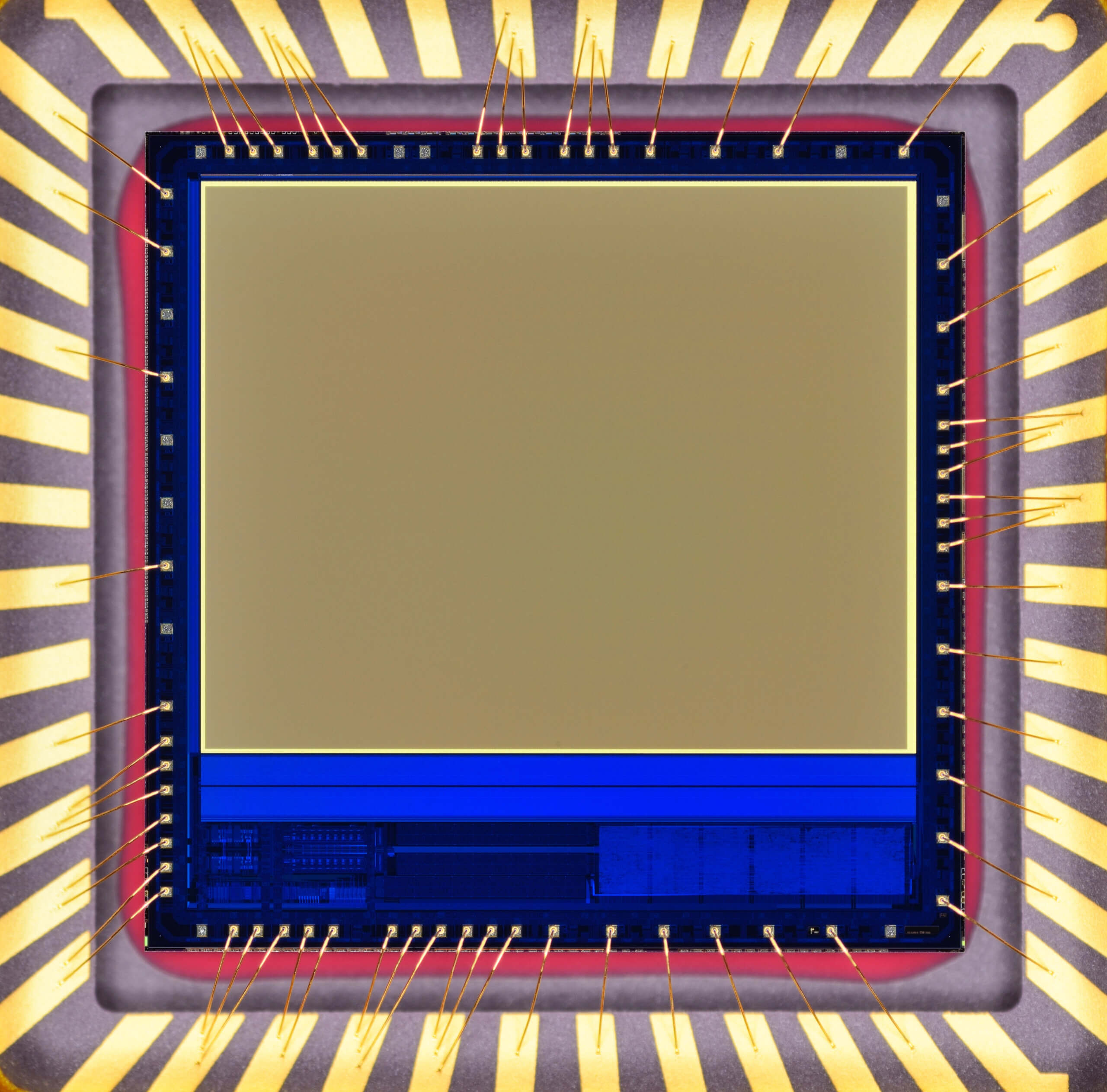
InGaAs FPAs Epi-wafers

InGaAs is a compound semiconductor whose optical properties can be tailored by varying the amounts of Indium, Gallium, Arsenic, and Phosphorus in its structure. Changing these proportions affects both the band gap energy and the lattice size, which plays a crucial role in managing strain within the layered epitaxial design on substrates such as InP.

An InGaAs FPA epi-wafer refers to an epitaxially grown semiconductor wafer designed for the fabrication of focal plane arrays (FPAs) based on Indium Gallium Arsenide (InGaAs), optimized for light detection in the near-infrared (NIR) spectrum. InGaAs FPA epi-wafers from VIGO Photonics are ideal for applications where traditional silicon detectors fall short due to limited NIR sensitivity. These include low-light and nighttime imaging, NIR spectroscopy for chemical and biological analysis, remote sensing in environmental, agricultural, and geological studies, as well as semiconductor inspection processes where NIR detection enhances defect identification and quality control.